Introduction
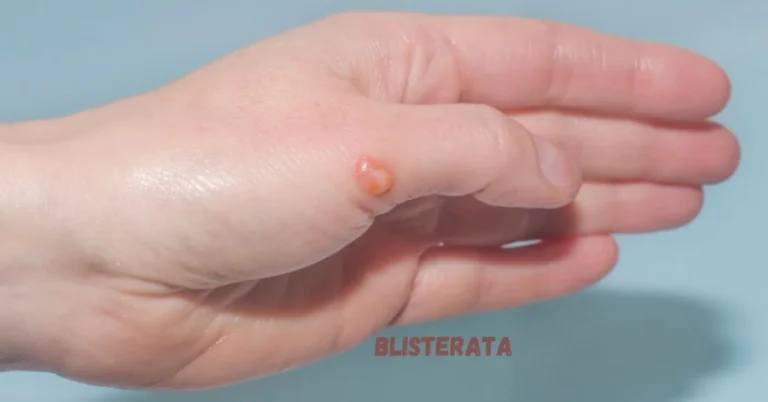
Blisterata, a dermatological condition characterized by the formation of blisters on the skin, remains a perplexing ailment for many. Despite its prevalence, comprehensive understanding of its etiology, symptoms, and treatment options is still lacking. This article endeavors to delve into the intricacies of Blisterata, shedding light on its various aspects to empower individuals with knowledge about this condition.
What is Blisterata?
Blisterata, also known as blister dermatitis, is a dermatological disorder characterized by the development of fluid-filled blisters on the skin’s surface. These blisters can vary in size, ranging from small vesicles to large bullae, and may occur singularly or in clusters. The condition can manifest anywhere on the body, including but not limited to the hands, feet, arms, legs, and torso.
Causes of Blisterata
The precise etiology of Blisterata remains elusive, as it can arise from a multitude of factors, both internal and external. Some common causes include:
Friction and Pressure: Prolonged friction or pressure on the skin, such as wearing ill-fitting footwear or engaging in repetitive activities, can lead to the formation of blisters.
Burns and Trauma: Thermal burns, chemical burns, or physical trauma to the skin can result in blister formation as the body’s natural response to injury.
Allergic Reactions: Contact with irritants or allergens, such as certain chemicals, plants, or medications, can trigger an allergic reaction, leading to blister formation.
Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections of the skin, such as herpes simplex or impetigo, can cause blisters as part of the body’s immune response to the invading pathogens.
Autoimmune Disorders: Certain autoimmune conditions, such as pemphigus or bullous pemphigoid, can cause the immune system to attack healthy skin cells, resulting in blister formation.
Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have an inherent predisposition to developing Blisterata due to genetic factors, although specific genes associated with the condition are still being researched.
Symptoms of Blisterata
The hallmark symptom of Blisterata is the presence of fluid-filled blisters on the skin’s surface. However, the condition may also present with additional symptoms, depending on the underlying cause:
Pain or Discomfort: Blisters may be accompanied by pain, tenderness, or discomfort, especially if they rupture or become infected.
Itching or Burning Sensation: Some individuals may experience itching or a burning sensation in the affected area, particularly in cases involving allergic reactions or infections.
Redness and Inflammation: The skin surrounding the blisters may appear red, inflamed, or irritated, indicating an immune response to the underlying cause.
Fever and Malaise: In cases where Blisterata is caused by an infectious agent or autoimmune disorder, systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or malaise may also be present.
Treatment Options for Blisterata
| Treatment Option | Description |
| Topical Therapies | Application of soothing ointments or dressings to alleviate discomfort and promote blister healing. |
| Oral Medications | Prescription of oral medications such as NSAIDs, antihistamines, or antibiotics for severe cases. |
| Protective Measures | Implementation of measures to protect the skin from further irritation or trauma. |
| Immune-Modulating Therapies | Administration of immunosuppressive medications or biologic agents for autoimmune-related Blisterata. |
| Pain Management | Use of pain relievers or topical anesthetics to alleviate discomfort during the healing process. |
Diagnosis of Blisterata
Diagnosing Blisterata involves a thorough medical evaluation, including:
Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the affected skin and inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any recent exposures or predisposing factors.
Skin Biopsy: In cases where the diagnosis is unclear or if an underlying autoimmune disorder is suspected, a skin biopsy may be performed to examine tissue samples under a microscope.
Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, swabs, or cultures may be conducted to identify any infectious agents or underlying autoimmune markers contributing to Blisterata.
Treatment Options for Blisterata
Treatment for Blisterata focuses on addressing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Depending on the severity and etiology of the condition, treatment options may include:
Topical Therapies: Applying topical ointments, creams, or dressings containing soothing ingredients such as aloe vera, calendula, or zinc oxide can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing of the blisters.
Oral Medications: In cases involving severe pain, inflammation, or infection, oral medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antihistamines, or antibiotics may be prescribed.
Protective Measures: Protecting the affected skin from further irritation or trauma, such as wearing cushioned footwear, using padded gloves, or avoiding exposure to known allergens, can aid in preventing recurrent blisters.
Immune-Modulating Therapies: For individuals with autoimmune-related Blisterata, immunosuppressive medications or biologic agents may be prescribed to modulate the immune response and reduce blister formation.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or topical anesthetics may be recommended to alleviate discomfort associated with Blisterata, particularly during the healing process.
Prevention Strategies for Blisterata
While some causes of Blisterata may be unavoidable, certain preventive measures can help minimize the risk of developing this condition:
Proper Footwear: Wearing well-fitted, comfortable footwear and using protective padding or bandages can reduce the risk of friction-induced blisters, especially during physical activity.
Skin Protection: Using gloves or protective clothing when handling chemicals or engaging in activities that may expose the skin to irritants or allergens can help prevent contact dermatitis and blister formation.
Hygiene Practices: Maintaining good hygiene, such as keeping the skin clean and dry, can help prevent bacterial or fungal infections that may lead to blister formation.
Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known allergens or irritants, such as certain skincare products or environmental triggers, can help prevent allergic reactions and subsequent blister development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Blisterata
1. What is Blisterata?
Blisterata, also known as blister dermatitis, is a dermatological condition characterized by the formation of fluid-filled blisters on the skin’s surface. These blisters can vary in size and may occur singularly or in clusters.
2. What causes Blisterata?
Blisterata can be caused by a variety of factors, including friction and pressure on the skin, burns or trauma, allergic reactions to irritants or allergens, infections (bacterial, viral, or fungal), autoimmune disorders, and genetic predisposition.
3. What are the symptoms of Blisterata?
The primary symptom of Blisterata is the presence of fluid-filled blisters on the skin. Additional symptoms may include pain or discomfort, itching or burning sensation, redness and inflammation of the surrounding skin, and in some cases, systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise.
4. How is Blisterata diagnosed?
Diagnosing Blisterata typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider, including a review of the patient’s medical history. In some cases, a skin biopsy, laboratory tests (such as blood tests or cultures), or other diagnostic procedures may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and identify any underlying causes.
5. What are the treatment options for Blisterata?
Treatment for Blisterata aims to address the underlying cause, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include topical therapies (such as ointments or creams), oral medications (such as NSAIDs or antibiotics), protective measures (to prevent further irritation or trauma), immune-modulating therapies (for autoimmune-related Blisterata), and pain management strategies.
Conclusion
Blisterata poses a significant challenge for both patients and healthcare providers due to its diverse etiology and variable presentation. By gaining a deeper understanding of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms effectively and reduce the risk of recurrent episodes. Through further research and collaboration within the medical community, we can continue to unravel the enigma of Blisterata and improve outcomes for those affected by this dermatological disorder.
Read More: Kingymab: The Ultimate Workout Trend Taking the Fitness World by Storm